Robot Description
DiffBot Robot Description
The description of the 2WD robot will be created in its own package named diffbot_description.
The description uses URDF and xacro.
For this we create a package with catkin create pkg PKG_NAME [--catkin-deps [DEP [DEP ...]]]:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Because this package contains only descriptions and launch files it doesn't require any dependencies.
According to ROS conventions we create the following folders where the individual files realted to the robot description will be placed:
1 | |
The urdf folder will be used to keep the urdf and xacro files.
The meshes folder keeps the meshes that are included in the urdf file, and the launch folder keeps the ROS launch files.
Robot Model
To model the two wheeled differential drive robot we follow REP-120.
It states to use a base_link and a base_footprint. The resulting description files can be found in the diffbot_description package.
Required Tools
To check a urdf file we can make use of the tools check_urdf and urdf_to_graphiz in the liburdfdom-tools debian package.
Install it with the following command:
1 | |
First we need to convert the robot description of DiffBot, which is present as xacro file, to a urdf file by issuing the following command:
1 | |
After we've created the urdf from the xacro file we can check the urdf files for errors with:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
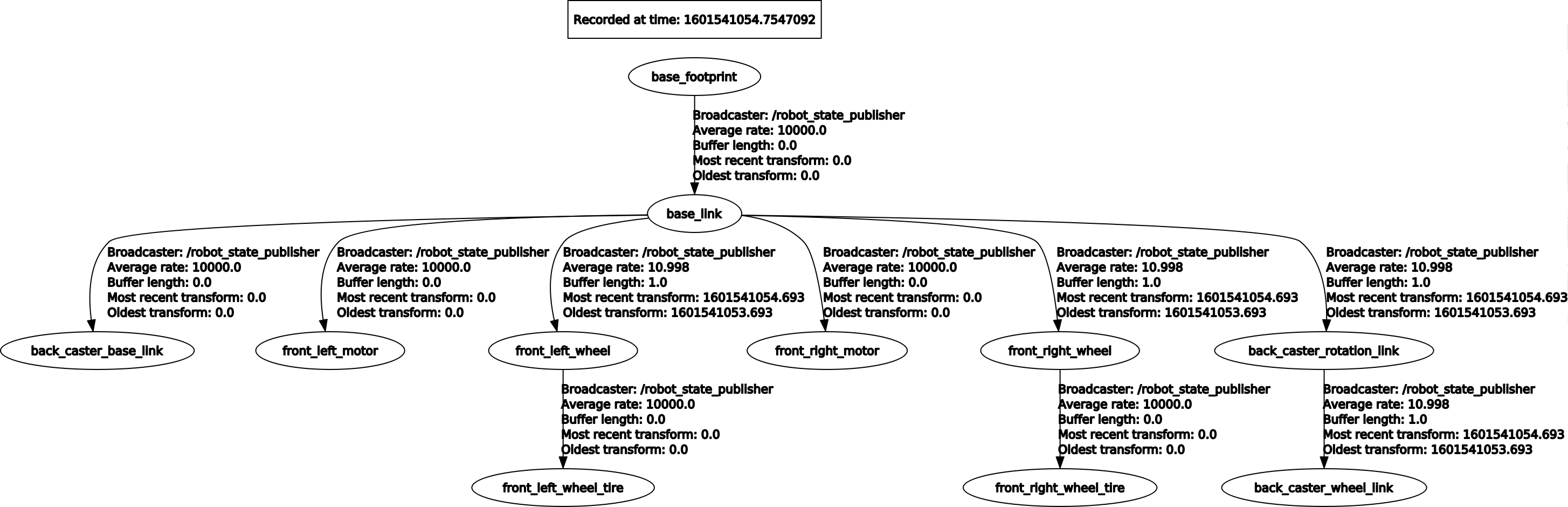
It is also helpful to output a graphviz diagram of the robot model:
1 2 3 4 | |
To visualize the 3D model in RViz we first need to install the joint-state-publisher-gui which was separated from non-gui joint-state-publisher. There exists a debian package which can be installed with the following command:
1 | |
After installing the required dependency, the view_diffbot.launch launch file can be executed using roslaunch command:
1 | |
According to the launch file's configuration, this will show the robot in RViz together with the joint-state-publisher-gui to set the joint values:
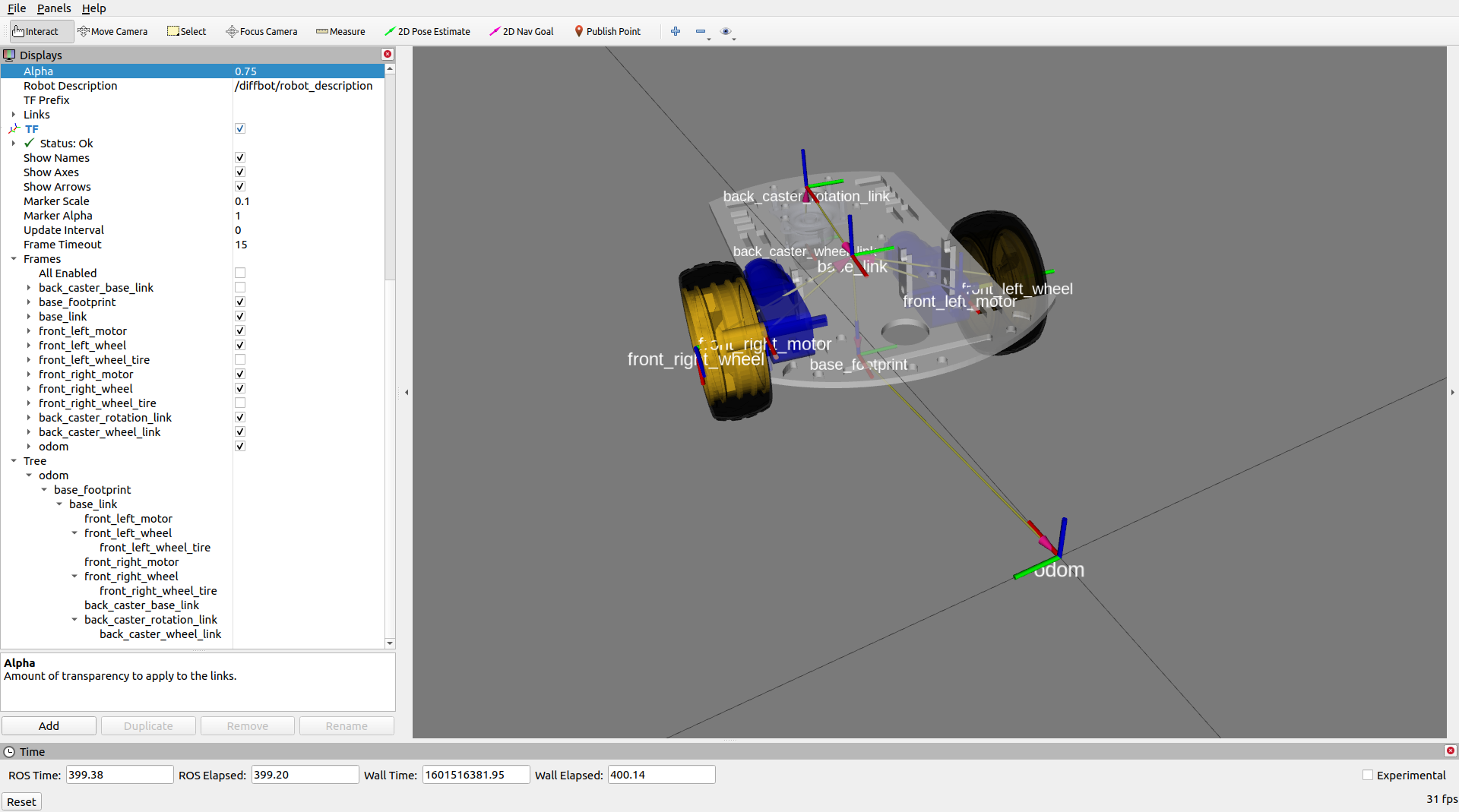
With the robot descripton loaded on the ROS parameter server, it's possible to use the TF Tree rqt plugin to display the transformation tree (see image above).
In the next section, Gazebo Simulation, the robot model is prepared for simulation inside of Gazebo.
URDF in Gazebo
http://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=ros_urdf&cat=connect_ros#Tutorial:UsingaURDFinGazebo