Navigation
DiffBot Navigation Package
1 2 3 4 5 | |
We also need the following ROS packages that can be installed from the ROS Ubuntu packages:
1 | |
After this we create the required launch files and parameter configurations. These will be used for the simulation and the real robot. First we focus on the simulation in Gazebo.
Launch files
All launch files are in the folder named launch of the diffbot_navigation package.
Inside the move_base.launch it is important to remap the following topics:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Parameter Configuration
The parameters for the navigation package go into the config (for some robots named param) folder.
Most of them can be changed during runtime using dynamic reconfigure with the rqt_reconfigure gui.
-
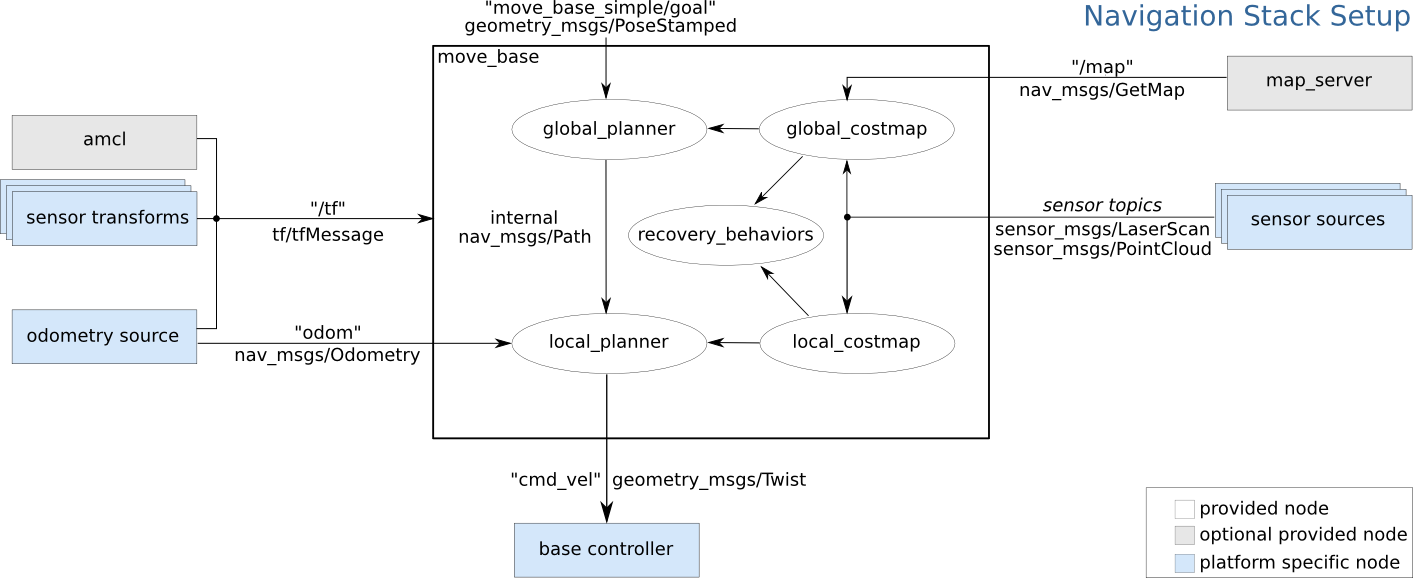
amcl: amcl is a probabilistic localization system for a robot moving in 2D. It implements the adaptive (or KLD-sampling) Monte Carlo localization approach (as described by Dieter Fox), which uses a particle filter to track the pose of a robot against a known map. -
map_server: provides themap_serverROS Node, which offers map data as a ROS Service. It also provides themap_savercommand-line utility, which allows dynamically generated maps to be saved to file. -
move_base: Themove_basepackage provides an implementation of an action (see theactionlibpackage) that, given a goal in the world, will attempt to reach it with a mobile base. Themove_basenode links together a global and local planner to accomplish its global navigation task. It supports any global planner adhering to thenav_core::BaseGlobalPlannerinterface specified in thenav_corepackage and any local planner adhering to thenav_core::BaseLocalPlannerinterface specified in thenav_corepackage. Themove_basenode also maintains two costmaps, one for the global planner, and one for a local planner (see thecostmap_2dpackage) that are used to accomplish navigation tasks. -
gmapping: This package contains a ROS wrapper for OpenSlam's Gmapping. The gmapping package provides laser-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), as a ROS node called slam_gmapping. Using slam_gmapping, you can create a 2-D occupancy grid map (like a building floorplan) from laser and pose data collected by a mobile robot. slam_toolbox
Examples - TurtleBot3 Navigation
Navigation in Gazebo with available Map
To navigate the robot in the simulation run the following command but make sure to first download the
turtlebot3_world
to your ~/.gazebo/models/ folder. This is required because the turtlebot3_world.world file references the turtlebot3_world model.
1 | |
This will spawn DiffBot inside the turtlebot3 world inside Gazebo and visualize the elements of the navigation stack in RViz.
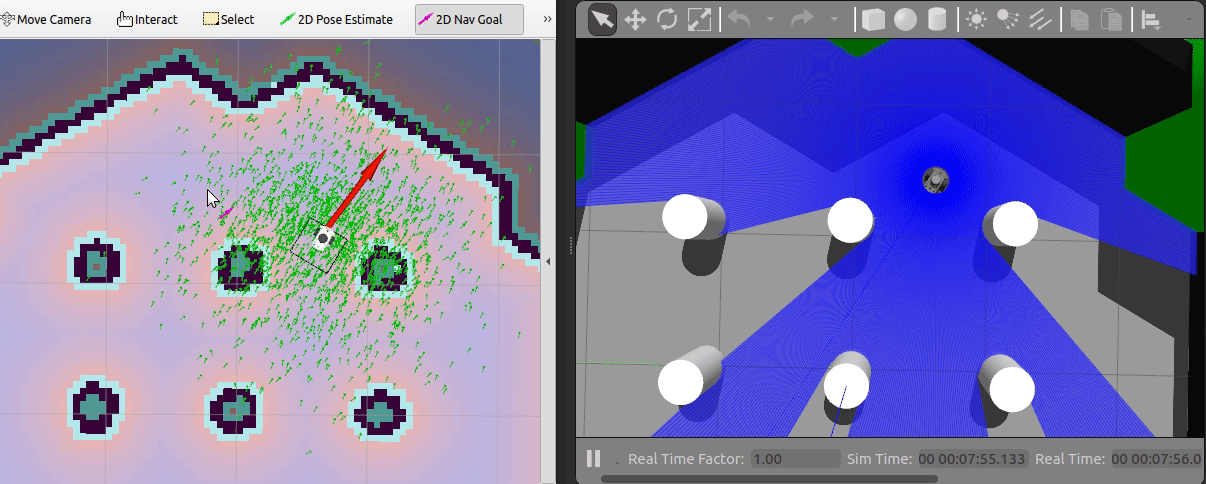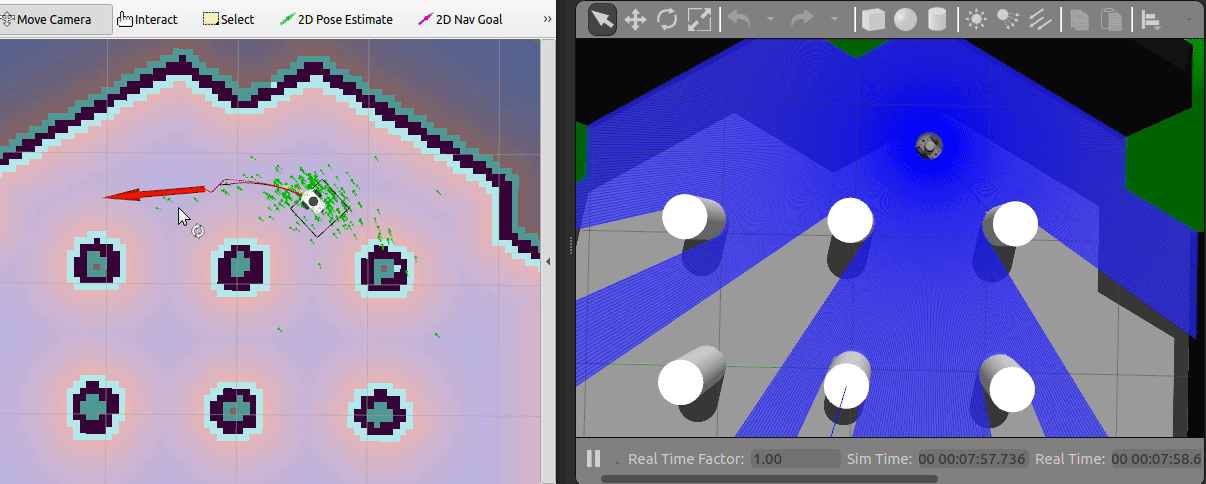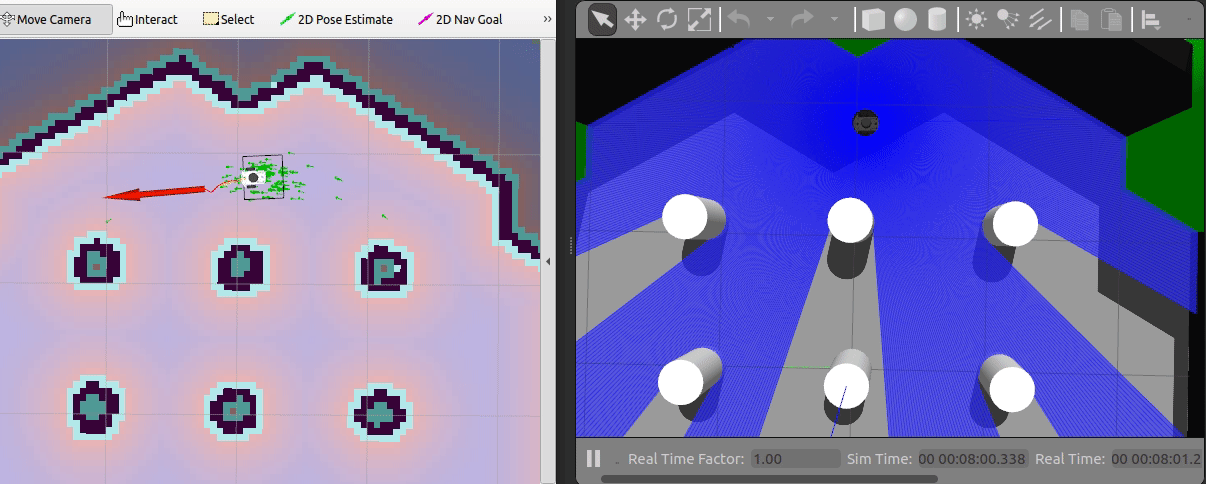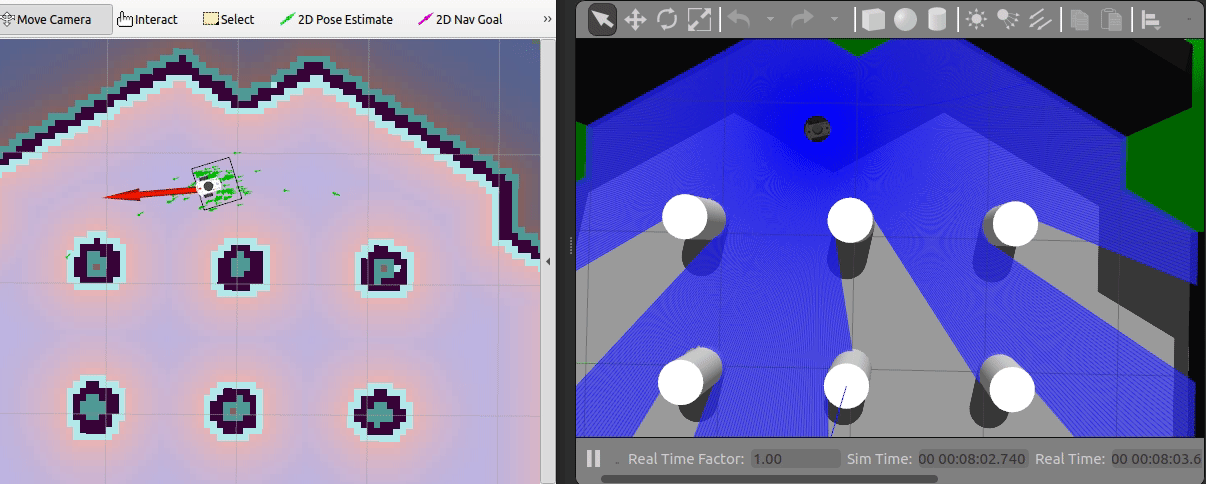
To navigate the robot using the default DWA planner in the known map,
coming from the running map_server, you can use the
2D Nav Goal in RViz.
Just select the navigation arrow to where the robot should move as shown in the animation above.
Note
The DWA local planner is working for differential drive robots, like DiffBot.
For other robots such as non-holonomic robots or other types of mobile robots (also differential drive robots) other planners can be used.
See for example teb_local_planner.
Resources
Global Planners:
- global_planner
Local Planners: - Difference between DWA and Base Local Planner - Difference between DWA and TEB Local Planner