Hardware Interfaces
The hardware interfaces provide an interface between the components (sensors and actuators) of the 2WD robot and its processing units, the Raspberry Pi 4 B (or the Nvidia Jetson Nano) and the microcontroller (in this case the Teensy 4.0).
USB
The Universial Serial Bus (USB) connections are required to connect the Single Board Computer (SBC) with the microcontroller. Using this connection, it is possible to communicate via rosserial.
Another USB connector is used for the RPLidar laser scanner.
Info
See the section USB Devices below to setup the required permissions and allow the communication between this interface.
Single Board Computer GPIO
Currently, one GPIO pin is used to connect the ultrasonic ranger.
The ultrasonic ranger uses just a single GPIO pin for communicating its measured distances. Therefore, we can use one of the GPIO pins such as physical pin 11.
Info
In case you are using LM393 speed sensors, instead of the encoders of the DG01D-E, the LM393 use a single digital GPIO pin each. These pins could be directly connected to the Raspberry Pi GPIOs and setup using software interrupts with the RPi.GPIO library. Alternatively they could be also connected to the pins of the microcontroller, e.g. Teensy. For this build the
Microcontroller Digital Pins
Four digital pins on the Teensy microcontroller are in use for the two quadrature encoders of the DG01D-E.
Info
See the diffbot_base package for the running software script to read the encoder ticks.
Single Board Computer I2C Connection
The I2C connections on the Raspberry Pi 4 B are used for multiple components such as the motor driver and the oled display.
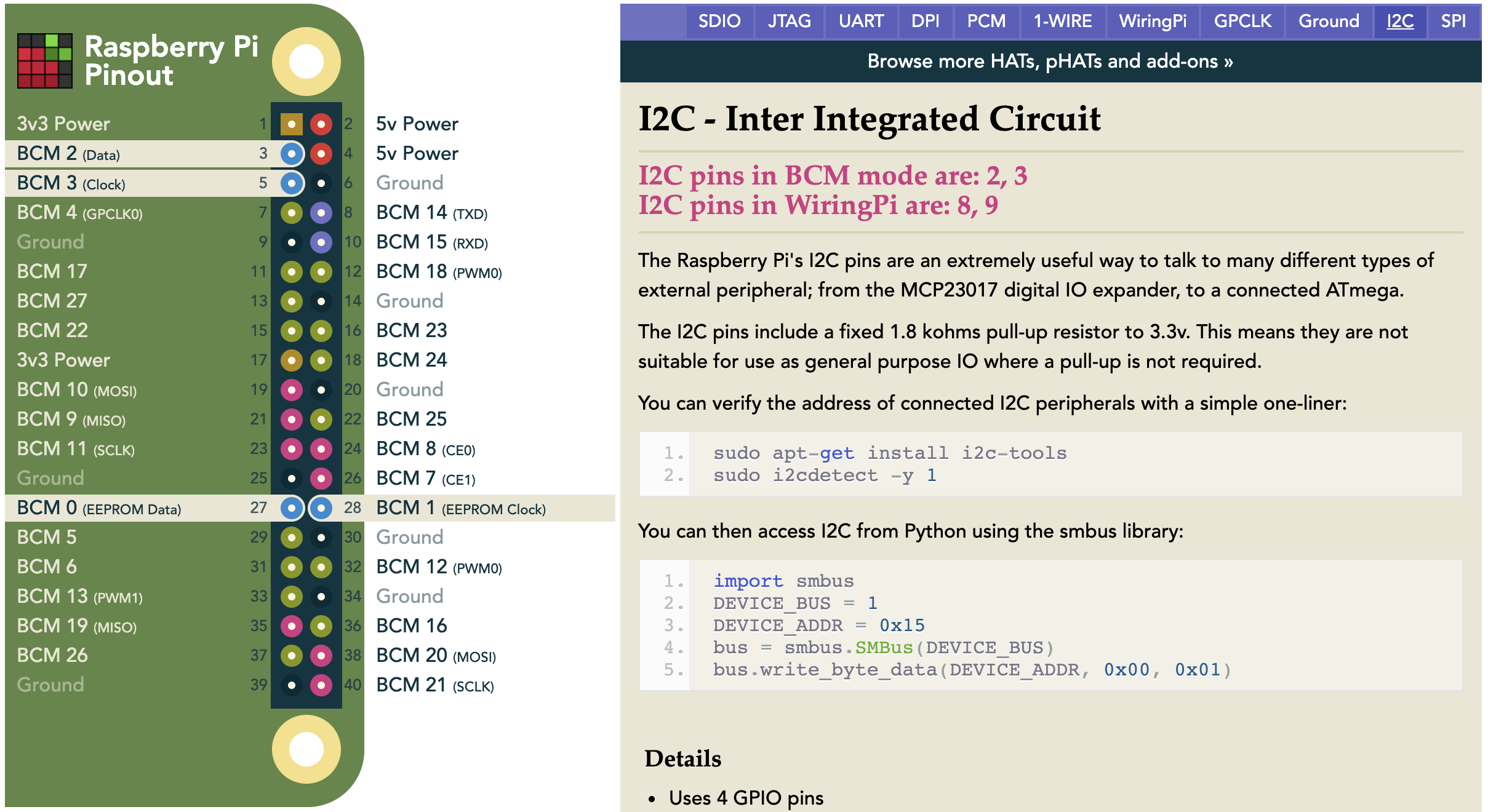
Using these ports on the Raspberry Pi 4 B, requires that we enable the I2C interface.
To do so, we will use the tool i2cdetect which requires that we install a tool on Ubuntu called i2c-tools:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
This i2cdetect tool is a userspace program to scan an I2C bus for devices
given a specific i2cbus argument which indicates the number or name of the I2C bus to be scanned,
and should correspond to one of the busses listed by i2cdetect -l. See also info i2cdetect for the manual page.
To test if the i2c ports are working we use the following commands:
1 2 3 4 | |
The ports are not setup correctly yet, which is why we need to enable the following two lines in the /boot/firmware/config.txt file:
1 2 | |
After rebooting the Raspberry Pi and entering the command again the following output will appear:
1 2 3 | |
Running as root using sudo will work (please read on, there is a better way):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
As mentioned there is a better way to access the i2c devices without using power user privileges. When issuing the following:
1 2 | |
we see that the /dev/i2c-0 device belongs to user root and i2c user group.
To get access without sudo we can add other users, requiering access to the i2c group with:
1 2 3 4 | |
After logging out and back in again the access will be granted and following output will come up:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
It outputs a table with the list of detected devices on the specified bus. In this case there are no connected devices on I2C bus 0.
Alternative setup using raspi-config
On Raspian Buster, the official Raspberry OS, we could use the `raspi-config` tool:fjp@ubuntu:~/git/2wd-robot$ sudo raspi-config
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B Rev 1.1 ┌──────────────────┤ Raspberry Pi Software Configuration Tool (raspi-config) ├───────────────────┐ │ │ │ 1 Change User Password Change password for the current user │ │ 2 Network Options Configure network settings │ │ 3 Boot Options Configure options for start-up │ │ 4 Localisation Options Set up language and regional settings to match your location │ │ 5 Interfacing Options Configure connections to peripherals │ │ 6 Overclock Configure overclocking for your Pi │ │ 7 Advanced Options Configure advanced settings │ │ 8 Update Update this tool to the latest version │ │ 9 About raspi-config Information about this configuration tool │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ <Select> <Finish> │ │ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Select the i2c option:
┌──────────────────┤ Raspberry Pi Software Configuration Tool (raspi-config) ├───────────────────┐ │ │ │ P1 Camera Enable/Disable connection to the Raspberry Pi Camera │ │ P2 SSH Enable/Disable remote command line access to your Pi using SSH │ │ P3 VNC Enable/Disable graphical remote access to your Pi using RealVNC │ │ P4 SPI Enable/Disable automatic loading of SPI kernel module │ │ P5 I2C Enable/Disable automatic loading of I2C kernel module │ │ P6 Serial Enable/Disable shell and kernel messages on the serial connection │ │ P7 1-Wire Enable/Disable one-wire interface │ │ P8 Remote GPIO Enable/Disable remote access to GPIO pins │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ <Select> <Back> │ │ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘And enable the interface:
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │ │ Would you like the ARM I2C interface to be enabled? │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ <Yes> <No> │ │ │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Confirm the activation and restart the RPi:
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │ │ The ARM I2C interface is enabled │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ <Ok> │ │ │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
USB Devices
Similar to accessing i2c devices, a non root user can use usb connections by adding it to the the dialout group:
1 2 3 4 | |